STL 容器 (一) - 基本介紹
layout: post title: '[C++] STL 容器 (一) - 基本介紹' keywords: C++, STL, Standard Template Library, Container, 標準模版函式庫, 容器
published: true
STL 是 C++ 提供的一套標準模板函式庫
全名是 Standard Template Library
因為是用 Template 實作的
所以裡面什麼都可以裝
內容索引(可以直接點)
Vector
Vector 可以看成是一個動態陣列
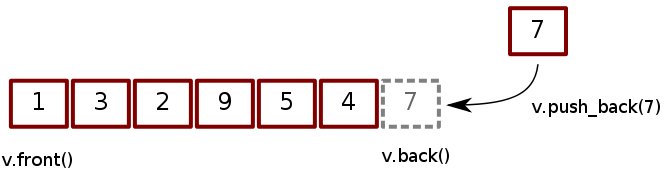
用法跟陣列很像,基本功能有 :
- push_back: 把一個值加到尾巴
- pop_back: 把尾巴的值移除掉
- size: 得到目前長度
- []: 得到某一個位置的值
範例 1
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main(){
vector<int> vec; // 宣告一個裝 int 的 vector
// 現在 vec 是空的
vec.push_back(10);
vec.push_back(20); // 經過三次 push_back
vec.push_back(30); // vec 是 [10, 20, 30]
int length = vec.size(); // length = 3
for(int i=0 ; i<length ; i++){
cout << vec[i] << endl; // 輸出 10, 20, 30
}
}
範例 2
int main(){
vector<int> vec;
for(int i=0 ; i<5 ; i++){
vec.push_back(i * 10); // [0, 10, 20, 30, 40]
}
for(int i=0 ; i<vec.size() ; i++){
cout << vec[i] << endl; // 輸出 0, 10, 20, 30, 40
}
}
範例 3
int main(){
vector<int> vec;
for(int i=0 ; i<5 ; i++){
vec.push_back(i * 10); // [0, 10, 20, 30, 40]
}
vec.pop_back(); // 移除 40
vec.pop_back(); // 移除 30
for(int i=0 ; i<vec.size() ; i++){ // vec.size() = 3
cout << vec[i] << endl; // 輸出 0, 10, 20
}
}
Vector 的優點
- 宣告時可以不用確定大小
- 可以 Random Access
Vector 的缺點
- 在內部進行刪除時效率很低
Queue
Queue 就像是排隊買東西
只能往尾巴排,然後從頭出來

基本功能有:
- push: 把一個值加到尾巴
- pop: 把第一個值移除掉
- back: 得到尾巴的值
- front: 得到頭的值
範例 1
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main(){
queue<int> q; // 一個空的 queue
q.push(10);
q.push(20);
q.push(30); // [10, 20, 30]
cout << q.front() << endl; // 10
cout << q.back() << endl; // 30
q.pop(); // [20, 30]
cout << q.size() << endl; // 2
}
範例 2
int main(){
queue<int> q; // 一個空的 queue
for(int i=0 ; i<5 ; i++){
q.push(i * 10);
} // [0, 10, 20, 30, 40]
while(q.size() != 0){
cout << q.front() << endl;
q.pop();
} // 依序輸出 0 10 20 30 40
}
Queue 的優點
- 可以快速的把頭的值拿掉
Queue 的缺點
- 只能操作頭跟尾
Stack
Stack 就是一疊盤子
只能拿走最上面的
或是繼續往上疊

基本功能有:
- top: 得到最上面的值
- push: 再拿一個盤子往上疊
- pop: 拿掉最上面的盤子
範例
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main(){
stack<int> s;
s.push(10); // | 30 |
s.push(20); // | 20 | 疊三個盤子
s.push(30); // |_10_| 10 在最下面
for(int i=0 ; i<s.size() ; i++){ // s.size() = 3
cout << s.top() << endl;
s.pop();
} // 輸出 30, 20, 10
}
Stack 的優點
- 操作很簡單(只有疊上去跟拿下來XD)
Stack 的缺點
- 只能操作最上面的那個值
Set
Set 就是集合
基本功能有:
- insert: 把一個數字放進集合
- erase: 把某個數字從集合中移除
- count: 檢查某個數是否有在集合中
範例
#include <set>
using namespace std;
int main(){
set<int> mySet;
mySet.insert(20); // mySet = {20}
mySet.insert(10); // mySet = {10, 20}
mySet.insert(30); // mySet = {10, 20, 30}
cout << mySet.count(20) << endl; // 存在 -> 1
cout << mySet.count(100) << endl; // 不存在 -> 0
mySet.erase(20); // mySet = {10, 30}
cout << mySet.count(20) << endl; // 0
}
Set 的優點
- 操作很簡單
- 可以快速檢查裡面有沒有某個元素
Set 的缺點
- 當 Set 裡面東西太多時會拖慢速度
Map
Map 就像是一個對應表
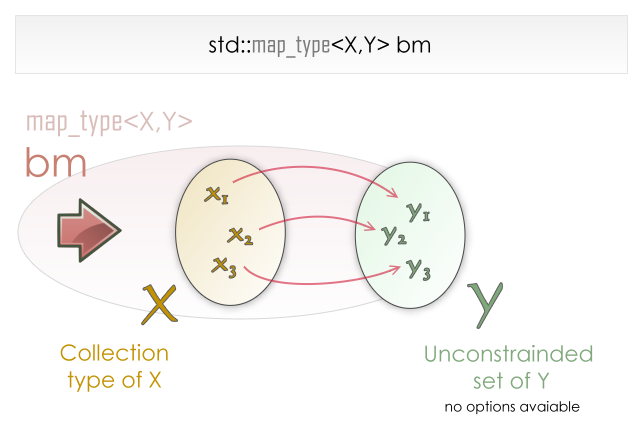
基本功能有:
- []: 得到對應的值
- count: 檢查某個值是否有對應值
範例 1
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main(){
map<string, int> m; // 從 string 對應到 int
// 設定對應的值
m["one"] = 1; // "one" -> 1
m["two"] = 2; // "two" -> 2
m["three"] = 3; // "three" -> 3
cout << m.count("two") << endl; // 1 -> 有對應
cout << m.count("ten") << endl; // 0 -> 沒有對應
}
範例 2
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main(){
map<string, int> m; // 從 string 對應到 int
m["one"] = 1; // "one" -> 1
m["two"] = 2; // "two" -> 2
m["three"] = 3; // "three" -> 3
cout << m["one"] << endl; // 1
cout << m["three"] << endl; // 3
cout << m["ten"] << endl; // 0 (無對應值)
}
Map 的優點
- 設定對應值很簡單
- 用很高的效率找到對應值
Map 的缺點
- 對應值越多會越慢
以上是基本的 STL 介紹
第二篇在這裡
講的東西會更進階一點
STL 有很多優點
練到能活用也要花一段時間
但是會了之後真的很好用