(四) 由16位元真實模式 (Real Mode) 進入32位元保護模式 (Protect Mode)
前三篇文章所展示的程式碼都是CPU執行於真實模式 (Real Mode)。然而,一般作業系統運行於保護模式 (Protect Mode),其記憶體定址最高可至4GB (32位元)。故本文先介紹real mode與protect mode記憶體定址的方式。
Real mode與Protect mode記憶體定址介紹
Figure 1展示real mode記憶體定址方式,其觀念在於將邏輯位址(Logical Address)的區段(Segment)位址向左位移4個位元,再將其所得的位址加上位移值,如此便能轉換成線性位址 (Linear Address)。至於,邏輯位址該如何表示呢? 其表示法為"Address of Segment:Offset" ,例如: CS:IP、SS:SP、DS:SI和ES:DI,詳情請參考x86 Assembly Language。Figure 1描述一個簡單邏輯位址轉換線性位址的例子,因此不再贅述。
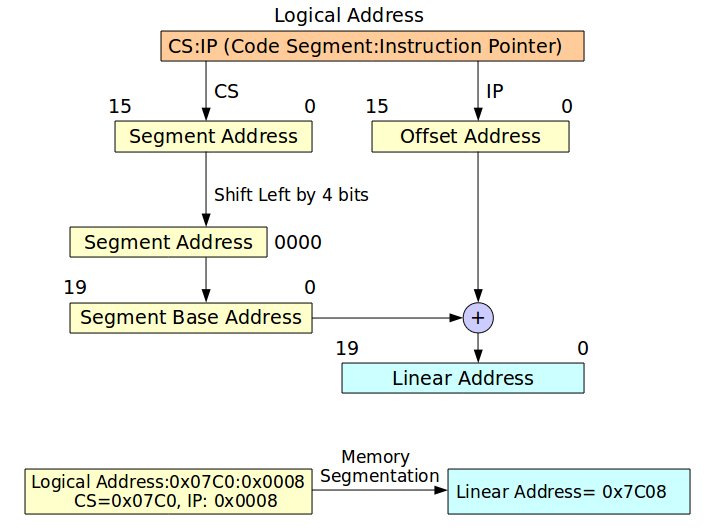
Figure 1. Memory Segmentation in Real Mode
Figure 2展示保護模式記憶體定址方式,其觀念在於將區段 (Segment)看成區段選擇器 (Segment Selector),用此選擇器索引出對應的Segment Descriptor,如此便能索引32位元的基底位址 (32-bit base address),然後再加上位移植,便能轉換成線性位址。
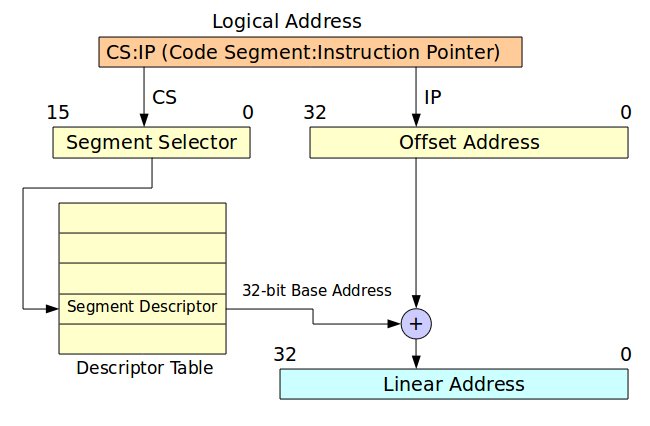
Figure 2. Memory Segment in Protect Mode
保護模式相關課題之介紹
此段落將著重介紹保護模式相關課題之介紹,包含介紹GDT/LDT (GDTR/LDTR)、Segment Descriptor、Segment Selector、 和Memory Management Register
Global and Local Descriptor Table (GDT and LDT)
當CPU運行於保護模式時,所有的記憶體存取都必須經由GDT或LDT,此表格 (GDT or LDT)存放最小單元便是Segment Descriptor。每一個Segment Descriptor都有對應的segment selector,用以索引出對應的Segment Descriptor。
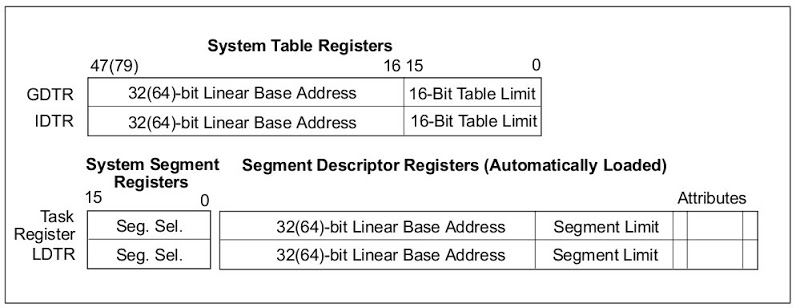
GDTR and LDTR (GDT Register and LDT Register)
GDTR與LDTR用以儲存GDT與LDT的起始位置,此設定必須在進入保護模式完成設定。Figure 3展示GDTR與LDTR格式,其中GDTR包含32位元的基底位址與16位元的長度限制。而LDTR多增加了16位元的segment selector。
Segment Descriptor
Segment Descriptor為Descriptor Table組成的基本元素,其長度為8位元組。如Figure 4所示,可分為三大類: 1. 32位元的基底位址 (Base Address), 2. 20位元的區段限制 (Segment Limit), 3. 區段屬性。細節請參考Intel 64 and IA-32 Architectures. Software Developer's Manual. Volume 3A
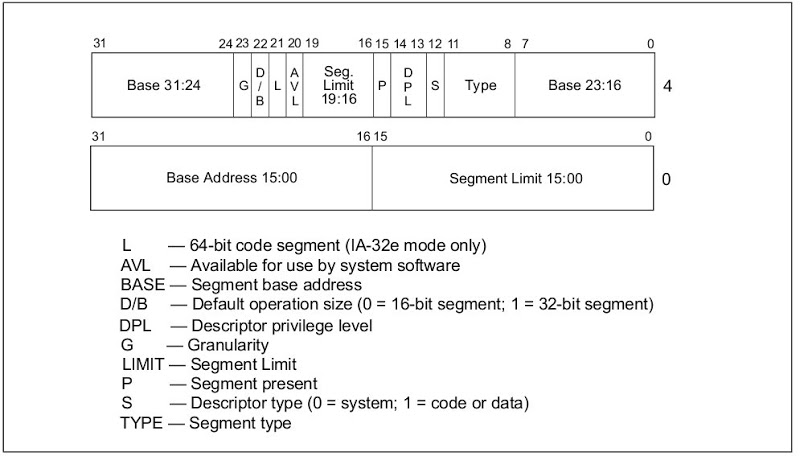
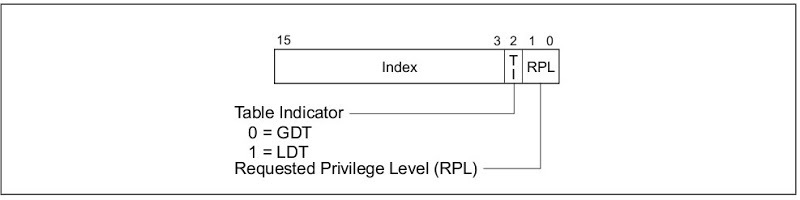
Segment Selector
Figure 5展示Segment Selector示意圖,其目的用來索引對應的Segment Descriptor。因Descriptor Index有13個位元,故Descriptor個數最大可至8192。
Boot Loader程式碼
/* boot_loader.S
*
* Copyright (C) 2010 Adrian Huang (adrianhuang0701@gmail.com)
*
* This code is intended to simulate a simplified boot loader. This boot
* loader loads 3 sectors into the physical memory and jumps the entry
* point of OS.
*
*/
.code16
.text
.set BOOT_SEG, 0x07C0 /* starting code segment (CS) of boot loader */
.set OS_SEG, 0x0900 /* code segment address of OS entry point */
.set OS_OFFSET, 0x0000 /* the offset address of OS entry point */
.global _start
_start:
# FAT12 file system format
jmp start_prog # jmp instruction
.byte 0x90
.ascii "ADRIAN " # OEM name (8 bytes)
.word 512 # Bytes per sector
.byte 1 # Sector per cluster
.word 1 # Reserved sector count: should be 1 for FAT12
.byte 2 # Number of file allocation tables.
.word 224 # Maximum number of root directory entries.
.word 2880 # Total sectors
.byte 0xf0 # Media descriptor:
.word 9 # Sectors per File Allocation Table
.word 18 # Sectors per track
.word 2 # Number of heads
.long 0 # Count of hidden sectors
.long 0 # Total sectors
.byte 0 # Physical driver number
.byte 0 # Reserved
.byte 0x29 # Extended boot signature
.long 0x12345678 # Serial Number
.ascii "HELLO-OS " # Volume Label
.ascii "FAT12 " # FAT file system type
.fill 18, 1, 0 # fill 18 characters with zero
start_prog:
# initialize the register with cs register
movw %cs, %ax
movw %ax, %ds
movw %ax, %es
movw %ax, %ss
xorw %sp, %sp
cld # clear direction flag
sti # set interrupt flag
# The following code is loaded three sectors (2-4th sectors from boot.bin)
# into the physical memory 0x8000-0x85FF.
movw $OS_SEG, %ax
mov %ax, %es # ES:BX-> destination buffer address pointer
movw $OS_OFFSET, %bx
movb $2, %cl # sector
cont:
movb $0x02, %ah # Read sectors from drive
movb $0x1, %al # Sectors to read count
movb $0x0, %ch # track
movb $0x0, %dh # head
movb $0, %dl # drive
int $0x13 # trigger a interrupt 0x13 service
jc fail # the clear flag is set if the operation is failed
mov %es, %ax
addw $0x20, %ax # move to the next sector
movw %ax, %es # move to the next sector
incb %cl
cmpb $3, %cl # has finished reading 3 sectors?
jbe cont # continue to read the sector
jmp os_entry # jump to OS entry point
fail:
movw $err_msg, %si
fail_loop:
lodsb
andb %al, %al
jz end
movb $0x0e, %ah
int $0x10
jmp fail_loop
os_entry:
ljmp $OS_SEG, $OS_OFFSET # jump to os context
end:
hlt
jmp end
err_msg:
.ascii "Reading sectors operation is failed!"
.byte 0
.org 0x1FE, 0x41 # fill the rest of characters with zero until the 254th character
# Boot sector signature
.byte 0x55
.byte 0xaa
作業系統程式碼
此作業系統程式碼運行於32位元保護模式,一開始定義三個Segment Descriptor (NULL, CODE32與VIDEO),其中VIDEO的基底位址為0xB8000,詳情請參考Printing to Screen。接著定義GDT的長度、定義Code32與VIDEO的segment selector、定義GDTPtr。
16位元real mode程式碼 (os_main)中,執行若干任務如下所述:
- 設定Code32的基底位址為PE_CODE32的起始位址
- 設定GDTPtr的基底位址為GDT的起始位址(也就是GDT_DESC_NULL)
- 開啟A20線路 (A20 Line)
- 將GDT的起始位址載入至GDTR暫存器
- 設定cr0暫存器的bit 0以便進入保護模式
- 使用ljmp指令跳至PE_CODE32程式碼
32位元保護模式程式碼 (PE_CODE32)利用Video segment selector將'H'字元顯示在螢幕,用以驗證程式運作之正確性。
/* os.S
*
* Adrian Huang (adrianhuang0701@gmail.com)
*
* This code is OS context for protected-mode.
*
*/
#include "pm.h"
.code16
.text
jmp os_main
# Segment descritors for GDT
GDT_DESC_NULL: SEG_DESC 0, 0, 0
GDT_DESC_CODE32: SEG_DESC 0, (PECode32Len - 1), (DESC_ATTR_TYPE_CD_ER | DESC_ATTR_D)
GDT_DESC_VIDEO: SEG_DESC 0xB8000, 0xFFFF, (DESC_ATTR_TYPE_CD_RW)
# The length of GDT
.set GdtLen, (. - GDT_DESC_NULL)
# Segment selectors for code segment and video output
.set SegSelectorCode32, (GDT_DESC_CODE32 - GDT_DESC_NULL)
.set SegSelectorVideo, (GDT_DESC_VIDEO - GDT_DESC_NULL)
# GDTR pointer
GDTPtr:
.2byte (GdtLen - 1) # Limit field
.4byte 0 # base field
# real-mode OS code
os_main:
mov %cs, %ax
mov %ax, %ds
mov %ax, %ss
mov %ax, %es
/* Set gdt for code segment */
InitSegDescriptor PE_CODE32, GDT_DESC_CODE32
/* Set GDTR */
xor %ax, %ax
mov %cs, %ax
shl $4, %eax
addl $GDT_DESC_NULL, %eax
movl %eax, (GDTPtr + 2)
/* Enable A20 line */
xor %ax, %ax
in $0x92, %al
or $2, %al
out %al, $0x92
cli
/* Load the GDT base address and limit from memory into the GDTR register */
lgdt GDTPtr
/* Enable protect mode */
movl %cr0, %eax
orl $1, %eax
movl %eax, %cr0
/* Jump to protected-mode OS code */
ljmp $SegSelectorCode32, $0
# protected-mode OS code
PE_CODE32:
.code32
/* Load Video segment selector */
mov $(SegSelectorVideo), %ax
mov %ax, %gs
/* Output the data */
movl $((80 * 10 + 0) * 2), %edi
movb $0xC, %ah
movb $'H', %al
mov %ax, %gs:(%edi)
jmp .
.set PECode32Len, (. - PE_CODE32)
os_msg:
.ascii "Welcome to OS context!"
.byte 0
.org 0x200, 0x41 # fill characters with 'A'. Sector 2
pm.h標頭檔
/* pm.h
*
* Adrian Huang (adrianhuang0701@gmail.com)
*/
.macro SEG_DESC Base, Limit, Attr
.2byte (\Limit & 0xFFFF)
.2byte (\Base & 0xFFFF)
.byte ((\Base >> 16) & 0xFF)
.2byte ((\Attr & 0xF0FF) | ((\Limit >> 8) & 0x0F00))
.byte ((\Base >> 24) & 0xFF)
.endm
.macro InitSegDescriptor OFFSET GDT_SEG_ADDR
xor %ax, %ax
mov %cs, %ax
shl $4, %eax
addl $(\OFFSET), %eax
movw %ax, (\GDT_SEG_ADDR + 2)
shr $16, %eax
movb %al, (\GDT_SEG_ADDR + 4)
movb %ah, (\GDT_SEG_ADDR + 7)
.endm
.set DESC_ATTR_TYPE_LDT, 0x82 /* LDT Segment */
.set DESC_ATTR_TYPE_CD_ER, 0x9A /* Code segment with Execute/Read */
.set DESC_ATTR_TYPE_CD_E, 0x98 /* Code segment with Execute Only */
.set DESC_ATTR_TYPE_CD_RW, 0x92 /* Data segment with R/W */
.set DESC_ATTR_D, 0x4000 /* 32-bit segment */
/* Selector Attribute */
.set SA_TIL, 0x4
.set SA_RPL0, 0x0
.set SA_RPL1, 0x1
.set SA_RPL2, 0x2
.set SA_RPL3, 0x3
編譯程式碼
下圖為編譯的Makefile。
LD=ld
CC=gcc
all: boot_loader.bin
boot_loader.bin: boot_loader.o os.o
${LD} -Ttext=0x7C00 -s $< -o $@ --oformat binary
${LD} -Ttext=0x0 -s os.o -o os.bin --oformat binary
cat os.bin >> $@
boot_loader.o:
${CC} -c boot_loader.S
os.o:
${CC} -c os.S
clean:
rm -f boot_loader.o os.o os.bin boot_loader.bin
其編譯訊息如下所示:
adrian@adrian-desktop:~/working/build_os/my_ex/04day/pe-orig-makefile$ make all
gcc -c boot_loader.S
gcc -c os.S
ld -Ttext=0x7C00 -s boot_loader.o -o boot_loader.bin --oformat binary
ld -Ttext=0x0 -s os.o -o os.bin --oformat binary
ld: warning: cannot find entry symbol _start; defaulting to 0000000000000000
cat os.bin >> boot_loader.bin
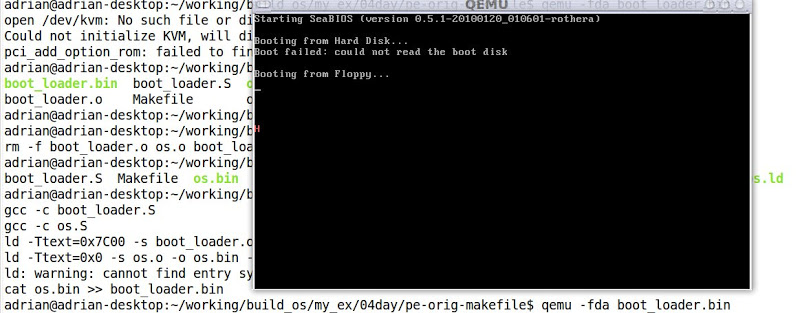
QEMU測試結果
【Reference】
- [1] Solrex - 使用開源軟體-自己動手寫作業系統
- [2] Intel 64 and IA-32 Architectures. Software Developer's Manual. Volume 3A
- [3] 30天打造OS!作業系統自作入門
- [4] Jserv's Blog
- [5] X86 開機流程小記
- [6] Linux assemblers: A comparison of GAS and NASM
- [7] linux-source-2.6.31