Linux Kernel: 強大又好用的list_head結構
Linux Kernel: 強大又好用的list_head結構 程式設計者在設計一個doubly linked list時,通常會在所宣告的結構裡宣告兩個結構指標,如下所示:
struct student {
char name[16];
int id;
struct student *next, *prev;
};
只要經由prev與next兩個結構指標,便能取得該doubly linked list所有資訊。
然而,Linux kernel並非引用此種作法。因此,Linux kernel定義一通用結構 (struct list_head, include/linux/list.h),用以實作doubly linked list,此結構相當簡單,如下所示:
struct list_head {
struct list_head *next, *prev;
};
所以物件student宣告為如下:
struct student
{
char name[16];
int id;
struct list_head list;
};
藉由list變數便能取得doubly linked list所有資訊。
list_head相關Marco與Function
這裡僅介紹較常用的macro與function,如欲進一步得知其它marco請參考include/linux/list.h
LIST_HEAD(name)
struct list_head name = { &(name), &(name) };
將next與prev指到自己,意味著此list為空的。
list_empty(const struct list_head *head)
retrun head->next == head;
檢查此list是否為空的。
list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
head->next->prev = new;
new->next = head->next;
new->prev = head;
head->next = new;
將資料加入至doubly linked list最前端。建議自己動手畫個圖,便可瞭解這幾個指標指到何處。
list_del(struct list_head *entry)
entry->next->prev = entry->prev;
entry->prev->next = entry->next;
將某一資料從中刪除。
list_entry(ptr,type,member)
((type *)((char *)(ptr)-(unsigned long)(&((type *)0)->member)))
透過此函式便能算出結構的起始位址,並做結構轉型便能取得結構的資料,此計算方式相當好用啊!!!
以struct student為例,如下所示:
(unsigned long)(&((struct student *)0)->member))) ==> 計算出list成員相對位址。通常看到這一個敘述,直覺地覺得應該會記憶體區段錯誤吧 (Segmentation Fault)!? 因為該敘述用NULL的pointer存取list成員,但在(struct student *)0)->member))前面加了&符號,就不會發生記憶體區段錯誤。因為&符號,只意味著存取list的位址,而不是資料, 經由此敘述便能取得list的位移植。如下圖所示,該敘述所得之位移植值為20。
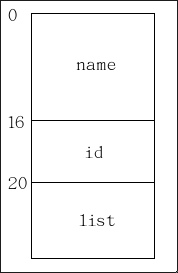
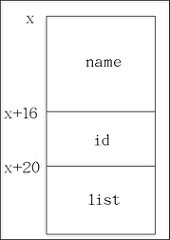
((type *)((char *)(ptr)-(unsigned long)(&((type *)0)->member))) ==> 取得位移植之後,再將list的位址減去位移植,便能取得該結構的起始位址,如下圖所示 (假設結構起始位址為x),最後再做結構轉型變大功告成。
list_for_each(pos, head)
for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next)
取得該doubly linked list所有資料。
- Makefile
obj-m += list_head_ex.o
KDIR=/lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
all:
make -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
clean:
make -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) clean
-list_head_ex.c
/*
* =============================================================================
*
* Filename: list_head_ex.c
*
* Description: Write a doubly linked list by using list_head structure
*
* Version: 1.0
* Created: Fri Oct 19 14:14:57 GMT 2007
* Revision: none
* Compiler: gcc
*
* Author: Adrian Huang
* Web Site: http://adrianhuang.blogspot.com/
*
* ============================================================================
*/
#include "list_head_ex.h"
int __init list_head_init(void)
{
struct list_head std_head, *next;
struct student sl[NR_STDS]; // student list
struct student *studentP; // student pointer
int idx;
/* init std_head */
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&std_head);
/* Check whether the std_head is empty */
if(list_empty(&std_head) == TRUE) {
printk(KERN_INFO "[Adrian] std_head is NULL\n");
}
/* Add each element to student head (std_head) */
for(idx=0;idx<sizeof(sl)/sizeof(struct student);idx++) {
sprintf(sl[idx].name, "Adrian Huang");
sl[idx].id = idx + 1;
list_add(&sl[idx].list, &std_head);
}
printk(KERN_INFO "======dump all elements of the list by invoking "
"'list_for_each'=========\n");
/* Traverse all elements of the list */
list_for_each(next, &std_head) {
studentP = (struct student *) list_entry(next, struct student, list);
printk(KERN_INFO "[Adrian] name: %s, id: %d\n",
studentP->name, studentP->id);
}
printk(KERN_INFO "\n======dump all elements of the list by invoking "
"'list_entry'=========\n");
/* Traverse all elements of the list and delete each of it */
for(idx=0;idx<sizeof(sl)/sizeof(struct student);idx++) {
studentP = (struct student *) list_entry(std_head.next,
struct student, list);
printk(KERN_INFO "[Adrian] name: %s, id: %d\n",
studentP->name, studentP->id);
list_del(std_head.next);
}
return 0;
}
void __exit list_head_exit(void)
{
;
}
module_init(list_head_init);
module_exit(list_head_exit);
- list_head_ex.h
/*
* =============================================================================
*
* Filename: list_head_ex.h
*
* Description: Write a doubly linked list by using list_head structure
*
* Version: 1.0
* Created: Fri Oct 19 14:17:58 GMT 2007
* Revision: none
* Compiler: gcc
*
* Author: Adrian Huang
* Web Site: http://adrianhuang.blogspot.com/
*
* =============================================================================
*/
#ifndef LIST_HEAD_EX_INC
#define LIST_HEAD_EX_INC
#include <linux/module.h> /* Needed by all modules */
#include <linux/kernel.h> /* Needed for KERN_INFO */
#include <linux/jiffies.h>
#include <linux/list.h> /* list_head structure */
#define NR_STDS 5
struct student {
char name[16];
int id;
struct list_head list;
};
typedef enum _Boolean { FALSE = 0, TRUE = 1 } LHBOOL; // list head boolean
#endif /* ----- #ifndef LIST_HEAD_EX_INC ----- */